Paper for Recycling (PfR) today is a mixture of different paper grades and each piece of paper in this mixture consists of different fibres. lt may also contain pigments or fillers, binder or additives and other components. ln addition, the paper products in the recovered paper mixture may have been coated, printed or upgraded by other means. The PfR may also contain non-paper products. Consequently, the mixture has to be processed in various ways to meet the quality criteria for the paper to be produced. Unlike the production of virgin-fibre pulps, in which wood is transformed into a fibre suspension, in recovered paper processing the aim is to separate the components that are not suitable for papermaking, and sometimes to restore or improve the quality of the fibres. Recycled fibre processing is therefore significantly more complex than virgin fibre production because the processes have to handle different types of fibre and also different types of contaminants and other substances detrimental for paper production.
Processing of PfR starts with the recovered paper delivered to the paper mill and ends with the pulp suspension ready for paper production stored in a chest. Between these two end points unit operations are arranged and the complexity of such systems depends on the quality requirements for the final pulp. Simpler systems as used for instance for corrugated material production where only particles larger than fibres have to be separated. In systems for the production of graphic or hygiene paper grades also fine particles like printing inks and filler material have to be separated and in many cases the pulp need to be bleached. While the unit operations are discussed in this section information about combining the unit operations to systems can be found in part Design of Processes. Figure 1 shows the basic layout of a so-called stock preparation system, which is the combination of unit operations to a process for PfR processing
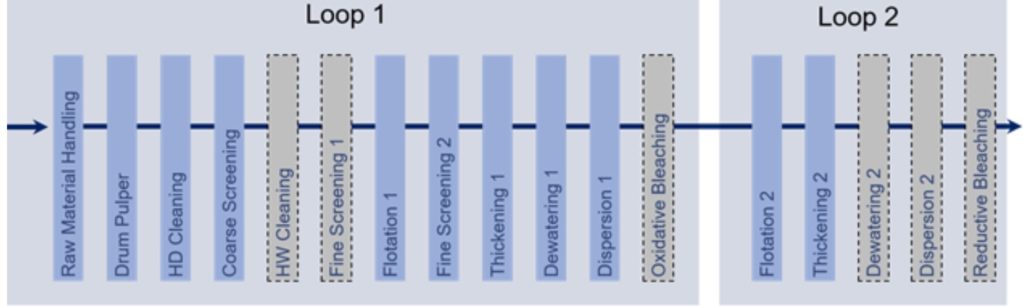
Figure 1 shows the main product stream, only. Real system are much more complex since some of the unit operations are installed several fold in cascaded or feed forward arrangements, water is circulated back in order to reduce water consumption and secondary processes for water treatment can be installed. These aspects are discussed in section Design of processes.

After the re-pulping step all unit operations are carried out with pulp fibre suspensions in a consistency range between about 0.8 % and 20 %. Therefore, some basic knowledge about the fluid mechanics of such fibre suspensions is important for understanding mechanisms in PfR processing. An introduction is given in article Fluid mechanics of pulp suspensions.
Source https://forestbiofacts.com/
Case
-
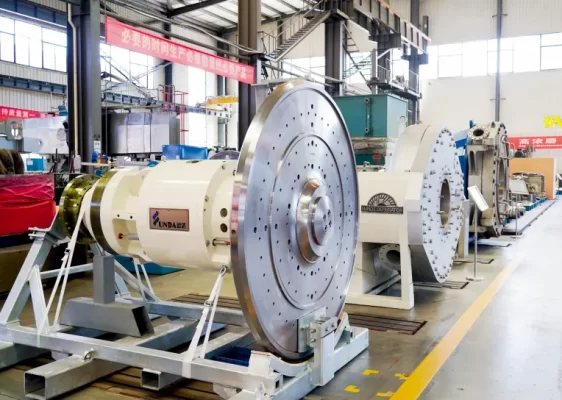 Yunda Supplies High-Consistency Refiner S2070 Drive Assembly to JSC, Belarus
Yunda Supplies High-Consistency Refiner S2070 Drive Assembly to JSC, Belarus
-
 Russia Khargi Packaging Paper Project
Russia Khargi Packaging Paper Project
-
 350,000 tpy Linerboard Project in Arkhangelsk, Russia
350,000 tpy Linerboard Project in Arkhangelsk, Russia
-
 KOA Vietnam 6600/1100 Packaging Paper Upgrade Project
KOA Vietnam 6600/1100 Packaging Paper Upgrade Project
-
 Smooth Shipment of Complete Thermo Mechanical Pulping Equipment for Thailand Precise Molding Project
Smooth Shipment of Complete Thermo Mechanical Pulping Equipment for Thailand Precise Molding Project
-
 Successful Delivery of the Refiner Repair Project Between Yunda and Guangzhou Paper Group
Successful Delivery of the Refiner Repair Project Between Yunda and Guangzhou Paper Group
-
 100,000 Tons Per Year Cultural Paper Project in Ethiopia
100,000 Tons Per Year Cultural Paper Project in Ethiopia
-
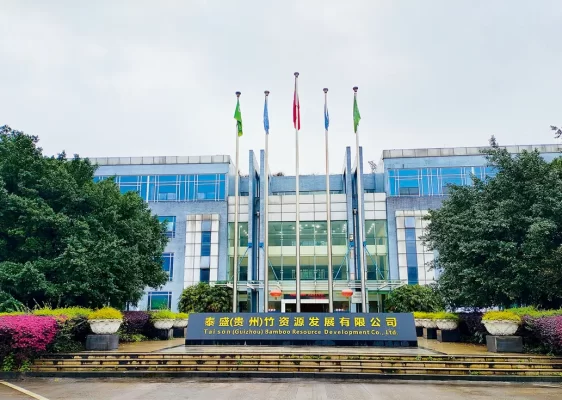 Taison (Guizhou) 160,000 tons tissue paper project
Taison (Guizhou) 160,000 tons tissue paper project
-
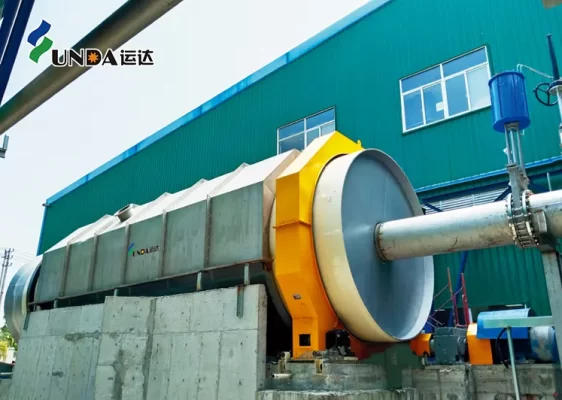 Taison Tissue Paper Project
Taison Tissue Paper Project
-
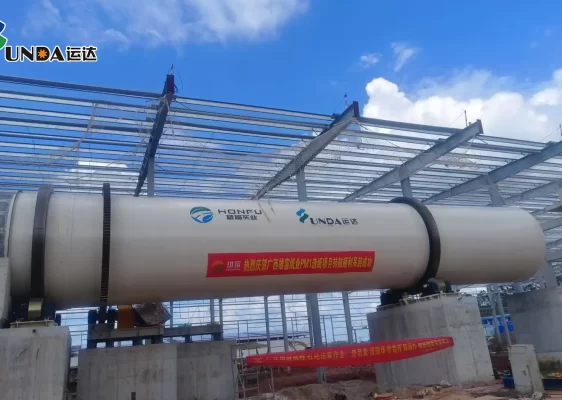 Guangxi Xiongfu Paper Project
Guangxi Xiongfu Paper Project









